Graphite electrodes are essential components in electric arc furnace (EAF) steelmaking, and they play a critical role in the production of high-quality steel. HP graphite electrodes are a specific type of graphite electrode that offers superior performance and durability. In this blog post, we will delve into the details and classification of HP graphite electrodes, exploring their unique properties and applications in the steel industry.
What are HP graphite electrodes?
HP graphite electrodes are high-performance graphite electrodes designed for use in EAF steelmaking. They are manufactured using high-quality raw materials, including petroleum coke, needle coke, and coal tar pitch, which are processed to achieve the desired physical and chemical properties. HP graphite electrodes are characterized by their high thermal conductivity, low electrical resistance, and excellent mechanical strength, making them ideal for withstanding the extreme conditions present in EAF steelmaking processes.
Classification of HP graphite electrodes
HP graphite electrodes are classified based on their physical dimensions, including diameter and length, as well as their specific properties such as thermal conductivity and current-carrying capacity. The classification of HP graphite electrodes is crucial for ensuring compatibility with different EAF systems and steelmaking processes. Common classifications of HP graphite electrodes include:
1. Diameter: HP graphite electrodes are available in various diameters ranging from 200mm to 700mm. The selection of electrode diameter depends on the specific requirements of the EAF system, such as power input, furnace design, and steel production capacity.
2. Length: HP graphite electrodes are manufactured in different lengths to accommodate varying furnace designs and operating conditions. Standard lengths range from 1600mm to 2900mm, with custom lengths available to meet specific customer needs.
3. Thermal conductivity: HP graphite electrodes exhibit high thermal conductivity, which allows for efficient heat transfer during the steelmaking process. The thermal conductivity of HP graphite electrodes is a key factor in determining their performance and energy efficiency in EAF steelmaking.
4. Current-carrying capacity: HP graphite electrodes are designed to carry high electrical currents required for the melting and refining of steel in EAFs. The current-carrying capacity of HP graphite electrodes is determined by their physical dimensions, material quality, and manufacturing process.
Properties of HP graphite electrodes
HP graphite electrodes possess several key properties that make them well-suited for use in EAF steelmaking. Some of the notable properties of HP graphite electrodes include:
1. High thermal conductivity: HP graphite electrodes have a high thermal conductivity, allowing for efficient heat transfer from the electrodes to the steel scrap in the EAF. This property ensures uniform heating and melting of the steel charge, leading to improved steel quality and energy efficiency.
2. Low electrical resistance: HP graphite electrodes exhibit low electrical resistance, enabling the efficient transfer of electrical energy from the power source to the EAF. This property contributes to the overall energy efficiency and cost-effectiveness of the steelmaking process.
3. Excellent mechanical strength: HP graphite electrodes are engineered to withstand the mechanical stresses and thermal shocks experienced during EAF steelmaking. Their superior mechanical strength ensures minimal electrode breakage and deformation, resulting in reliable and uninterrupted steel production.
4. Oxidation resistance: HP graphite electrodes demonstrate high resistance to oxidation at elevated temperatures, ensuring prolonged service life and minimal electrode consumption during steelmaking operations.
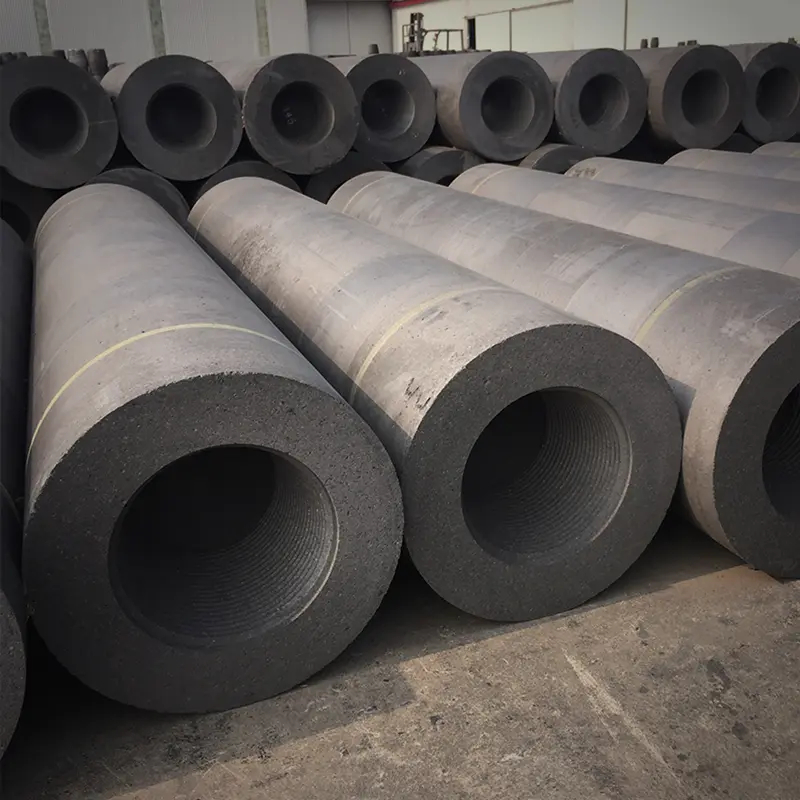

Applications of HP graphite electrodes
HP graphite electrodes find widespread applications in various steelmaking processes, including:
1. Electric arc furnace (EAF) steelmaking: HP graphite electrodes are extensively used in EAF steelmaking for melting and refining steel scrap to produce high-quality steel products. Their superior thermal conductivity and current-carrying capacity make them indispensable for efficient and cost-effective steel production.
2. Ladle furnace (LF) refining: HP graphite electrodes are employed in LF refining processes to adjust the chemical composition and temperature of liquid steel before casting. They facilitate precise control over the refining operations, ensuring the production of clean and homogenous steel grades.
3. Foundry applications: HP graphite electrodes are utilized in foundry applications for melting and alloying various metals and alloys, including cast iron, aluminum, and copper. Their high thermal conductivity and durability make them suitable for demanding foundry operations.
In conclusion, HP graphite electrodes are essential components in modern steelmaking processes, offering superior performance, durability, and efficiency. Their unique properties and diverse applications make them indispensable for achieving high-quality steel products while optimizing energy consumption and production costs in the steel industry.
Post time: 8 月-08-2024